Accident Modelling and Risk Analysis
Background
Process systems are prone to devastating accidents as they deal with hazardous material at high temperature, high pressure. Process plants are also characterized as complex systems where a dense cluster of pipes and equipment makes it more likely that a primary accident escalates into secondary accidents, leading to a chain of accidents or so-called domino effect. Thus, the implementation of preventive and mitigative safety measures is crucial to maintain the level of risk below the acceptance criteria. To this end, accident scenario modeling and quantitative risk analysis have widely been used to explore the root causes and possible consequences of an accident. Using these methods, not only the envisaged risk of an accident can be estimated, but the effect of relevant safety measures can be investigated.
 Objectives
Objectives
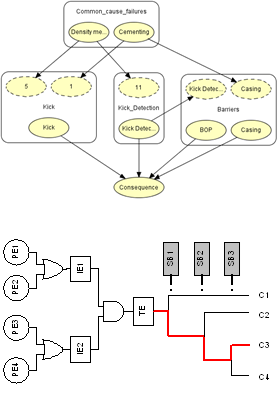
The main focus of Accident Modeling and Risk Analysis Section of SREG is on the research and development of methodologies for risk analysis and safety assessment of complex systems to address the needs of the industry in oil and gas and process facilities.
Current Research Areas
- Bayesian data analysis and predictions
- Application of accident precursor data in probability estimation and dependency analysis
- Application of physical reliability models and monitoring in dynamic risk analysis
- Bayesian networks
- Rare accident risk analysis
Principal Research Lead:
Research/Team Lead:
Nima Khakzad
Group Members:
Majeed Abimbola
Zhi Yuan
Related Publications since 2010:
- M. Abimbola, F. Khan, and N. Khakzad, Dynamic safety risk analysis of offshore drilling, Journal of Loss Prevention in the Process Industries 30 (2014), 74–85, DOI:10.1016/j.jlp.2014.05.002.
- C. T. Cloney, P. R. Amyotte, F. I. Khan, and R. C. Ripley, Development of an organizational framework for studying dust explosion phenomena, Journal of Loss Prevention in the Process Industries (2013).
- M. Abuswer, P. Amyotte, F. Khan, and L. Morrison, An Optimal Level of Dust Explosion Risk Management: Framework and Application, Journal of Loss Prevention in the Process Industries (2013).
- M Dadashzadeh, F Khan, R Abbassi, K Hawboldt (2013). Combustion Products Toxicity Risk Assessment in an Offshore Installation. Accepted in Journal of Process Safety and Environmental Protection.
- Khakzad N, Khan F, Amyotte P. Quantitative risk analysis of offshore drilling operations: a Bayesian approach. Safety Science 2013; 57: 108 – 117
- Rathnayaka, S., Khan, F.I., & Amyotte, P. (2013). Accident modeling and risk assessment framework for safety critical decision making: Application to deep-water drilling operation, Journal of Risk and Reliability, DOI: 10.1177/1748006X12472158
- M Dadashzadeh, R Abbassi, F Khan, & K Hawboldt (2013). Explosion modeling and analysis of BP Deepwater Horizon accident. Safety Science 57, 150-160
- Khakzad N, Khan F, Amyotte P. Dynamic safety analysis of process systems by mapping bow-tie into Bayesian network. Process Safety and Environmental Protection 2013; 91: 46 – 53
- Khakzad N, Khan F, Amyotte P. Risk-based design of process systems using discrete-time Bayesian networks. Reliability Engineering and System Safety 2013; 109: 5 – 17
- Khakzad N, Khan F, Amyotte P, Cozzani V. Domino effect analysis using Bayesian networks. Risk Analysis 2013; 33(2): 292-306
- Khakzad N, Khan F, Amyotte P. Dynamic risk analysis using bow-tie approach. Reliability Engineering and System Safety 2012; 104: 36 – 44
- Khakzad N, Khan F, Amyotte P. Safety analysis in process facilities: comparison of fault tree and Bayesian network approaches. Reliability Engineering and System Safety 2011; 96: 925 – 932
- Khakzad N, Firoozabadi B, Farhanieh B. Numerical investigation of steady density currents flowing down an incline using v2-f turbulence model. Journal of Fluids Engineering (Transactions of ASME) 2007; 129(9): 1172 – 1178
- Rathnayaka, S., Khan, F., and Amyotte, P. (2012). Accident modeling approach for safety assessment in an LNG processing facility. Journal of Loss Prevention in the Process Industry, 25. 414 – 423
- Keshavarz, G., Khan, F., and Hawboldt, K. (2011). Modeling of Pool Fires in Cold Regions. Fire Safety Journal. 1–10.
- Khakzad, N., Khan, F., and Amyotte, P. (2011). Safety analysis in process facilities: Comparison of fault tree and Bayesian network approaches. Reliability Engineering and System Safety, 96. 925 – 32.
- Rathnayaka, S., Khan, F.I. and Amyotte, P. (2011). SHIPP Methodology: Predictive Accident Modeling Approach. Part I: Methodology and Model Description. Process safety and Environmental Protection, 89(3). 151–164.
- Rathnayaka, S., Khan, F.I., and Amyotte, P. (2011). SHIPP Methodology: Predictive Accident Modeling Approach. Part II: Validation with case study. Process safety and Environmental protection, 89(2). 75 – 88
- Kalantarnia, M., Khan, F., and Hawboldt, K. (2010). Modeling of BP Texas Refinery Accident using Dynamic Risk Assessment Approach. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 88 (3).191-199.
- Ferdous, R., Khan, F., Sadiq, R., Amyotte, P., and Veitch, B. (2010) Fault and Event Tree Analyses for Process Systems Risk Analysis: Uncertainty Handling Formulations. Risk Analysis, 31(1). 86-107
- Kujath, M. F., Amyotte, P., and Khan, F. (2010). A Conceptual Offshore Oil And Gas Process Accident Model. Journal of Loss Prevention in the Process Industries, 23 (2). 323-330