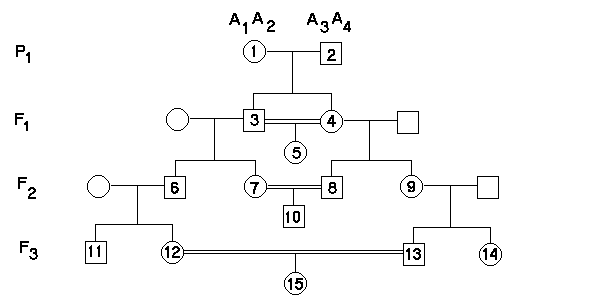
Inbreeding in pedigrees

Consanguinious
matings are those between related individuals (those
that
share a common ancestor), and are indicated by double lines
between pedigree symbols. The relatedness
(r)
of two individuals is the fraction of
alleles they share at all loci. The
offspring of a consanguinious mating are said to be inbred.
The inbreeding coefficient (F)
for an inbred individual is the probability that the individual has two
alleles identical by descent at a
locus.
Alleles are identical by descent if they are genetic copies of the same
allele in the common ancestor. These probabilites can be calculated by
following each allele through several generations.
For example, we can calculate the probability that individual #5, the product of a full-sib mating, has two alleles at the A locus that are identical by descent as F = 1/4 = 0.25. Other relatedness and inbreeding coefficients for typical consanguinious matings are shown below.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|