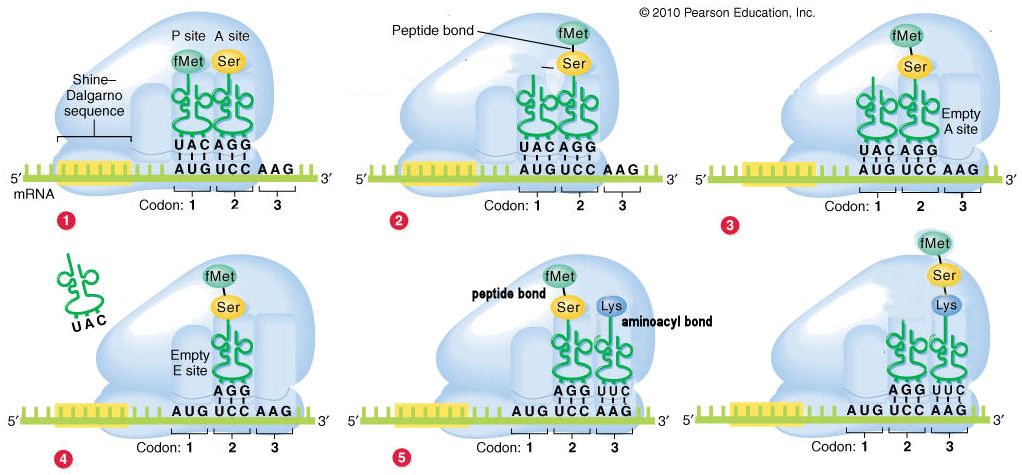
Elongation of
polypeptide
The order of sites
as EPA. (1) The fMet-tRNA starts the process in the
P site; subsequent charged tRNAs enter through the A site. (2) The fMet is cleaved trom the tRNA in the P site, and linked by a peptide bond to the amino acid in
the A site. (3) The tRNA in the P sites moves to the E site, and the tRNA in the A site with the
di-peptide moves to
the P site. (4) The uncharged tRNA is released. (5) A new charged tRNA enters the A site: note that at this point the
P site contains a peptidyl bond, and A site an aminoacyl bond. (Last) The dipeptide
is cleaved from the tRNA in
the P site, and linked by a
peptide to the amino acid in the A site
(as in step 2 above). The cycle continues
in this manner.
Transfer of
the amino acid from the first tRNA
to the second tRNA may at
first seem counter-intuitive. This however ensures that the original
amino terminus of the first amino acid always remains unmodified: thus
the polypeptide grows in the amino  carboxy (N
carboxy (N C).
C).