
Regulation of Gene Transcription: Part 2

Tissue-Specific Regulation of Transcription
Many enhancer elements in higher eukaryotes activate transcription in a tissue-specific manner, inducing gene expression in specific cell types (eg. Antibody genes have powerful enhancers which only operate in the B lymphocytes of the immune system).
Many enhancers are integral components of complex tissue-specific genetic circuits that underlie complex events in development in higher eukaryotes.
Tissue-specific regulation can occur in two ways:
1. The activator which binds to the enhancer is only present in some types of cells.
2. A tissue-specific repressor can bind to a silencer located very close to an enhancer, making the enhancer inaccessible to its transcription factor.
Regulation of some genes is fairly simple, being controlled by only a few sets of enhancers or repressors…
…but usually it is a very complex system of both enhancers and repressors, along with many tissue-specific regulators working together (in both space and time) to get the desired regulation of genes (very important in development).
The tissue-specific regulation of a gene can be, and often is very complex, requiring the action of many distantly located enhancer elements. It may be the many enhancer (and repressor) elements needed for tissue-specific gene regulation that accounts for the large size of eukaryotic genes.
Dissecting Regulatory Elements
The use of transgenic constructs (modified genes) to identify and characterize regulatory elements at distant locations.
Isolated pieces are incorporated to determine what tissue it controls, and which regulatory patterns it controls.
Genes are “sliced and diced” to locate specific regulatory elements
Regulatory Elements and Dominant Mutations
Properties of regulatory elements help us to understand the nature of gain-of-function mutations.
Gain-of-function dominant mutations can arise through the fusion of the regulatory elements of one gene to a structural RNA or protein-coding sequence of a different gene.
These can occur at breakpoints formed during chromosomal rearrangements (inversions, translocations, duplications, and deletions)
Enhancers can act at long distances; therefore if the enhancer of one gene is inserted with the transcription unit of another during rearrangement, misregulation may occur.
The enhancer located at one breakpoint is able to regulate the transcription of a gene at another breakpoint. This leads to misexpression of mRNA and can lead to gain-f-function dominant mutant phenotypes.
Example 1: Bar dominant eye-shape mutation in Drosophila
Example 2: Tab mutation in Drosophila
Gene fusions are a very important source of genetic variation. Through these chromosomal rearrangements gene expression can develop new patterns. These 2 phenomena together may play a very important role in the shifts of gene expression involved in the divergence and evolution of species.
These types of mutations affect development; however they may play an important role in the formation and progression of many cancers.
Structure and Function of Transcription Factors
The cellular environment is important to transcription regulation and transcription factors need to be responsive to it.
Many eukaryotic signals are intrinsic signals synthesized by the organism it self (not substrates or products of metabolic pathways).
These signals can send regional or global signals- we will focus on global signals, those which are sent from a “master command tissue” (ie. A gland), and sent through the blood stream to be received by the appropriate target tissue.
Many of these “global signals” are sequence-specific DNA-binding, and are crucial to gene regulation.
DNA-Binding Specificity of Regulatory Proteins
Cooperative Interactions and DNA-Binding Activity
Epigenetic Inheritance
Paramutation
Parental Imprinting
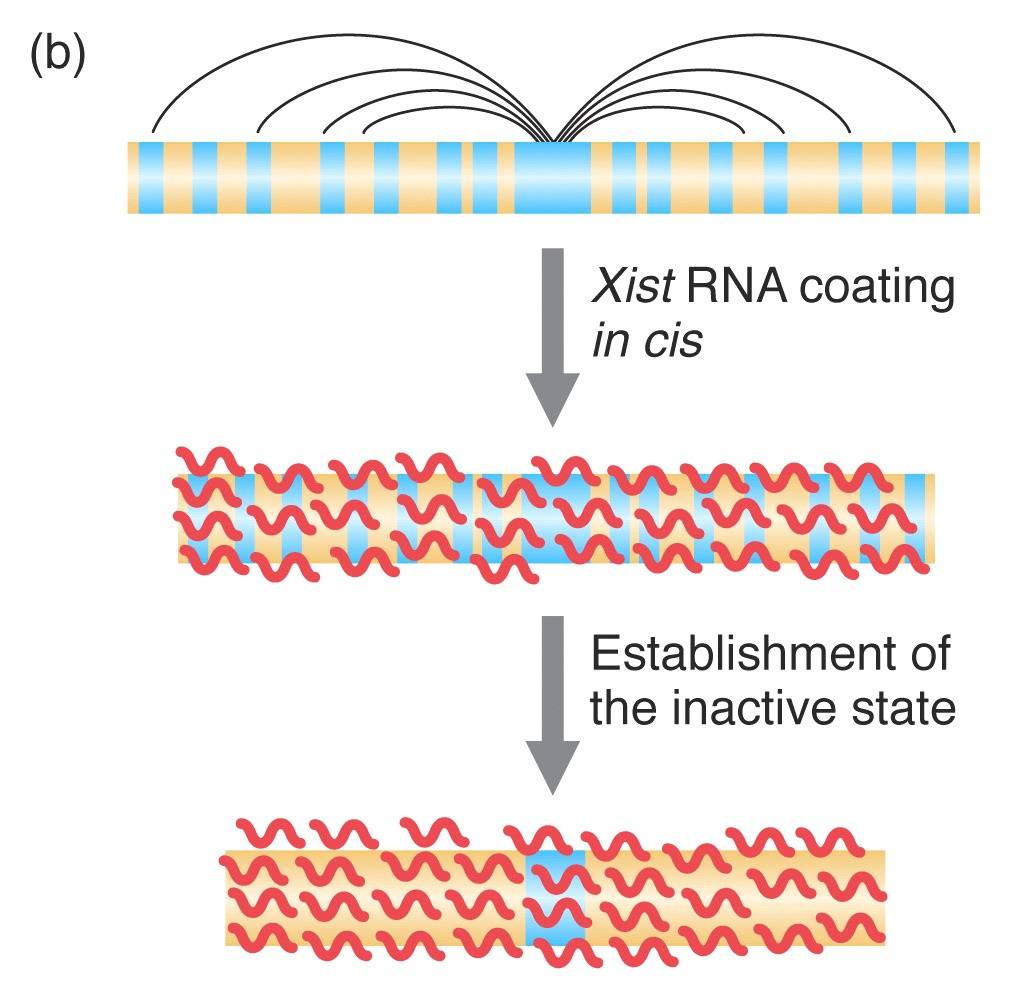
X-Activation in Mammals
Two aspects reflect imprinting
Transcription Regulation in the Era of Genomics
One Approach
Another Approach
Endocrine Regulation of Transcription Factor Activity
The endocrine system often acts as the tie between transcription regulation and the organism’s physiology, taking the role of major controller in transcription regulation.
The endocrine system is able to signal eukaryotic transcriptional factors in many tissues from a great distance through hormones released in the blood system, the most important being steroid hormones.
Examples:
Ovalbumin
Ovalbumin (egg-white protein) is specifically synthesized in response to high estrogen levels in the chicken oviduct, due to increased transcription of the ovalbumin gene.
Sex Hormones
Estrogen and testosterone, the male and female sex-determining hormones, respectively, are very important in transcription regulation and development.
Basically, the Y chromosome tells germ cells to develop into testes, which then produce the male (androgenic) steroid, testosterone.
The testosterone then acts as outlined previously, binding to androgen receptors which then act as specific transcription factors to activate male-specific gene expression.
Without testes, estrogen is produced instead of testosterone, and works in the same way to activate female-specific gene expression
Anabolic Steroids

Anabolic steroids are related to the hormone testosterone and act in much the same way, activating genes that contribute to muscular development, they also block the effects of cortisol on muscle, decreasing recovery time, hence the use by many athletes.
Anbolic steroids have many negative side effects, including at the genetics level. The prolonged use of anabolic steroids interferes with the body’s natural regulatory mechanisms, altering normal gene expression
Besides the genes which contol muscle development, many other genes are effected by the high levels of androgenic hormone, effecting the production of many proteins and tissues, mostly causing negative side effects after prolonged use.