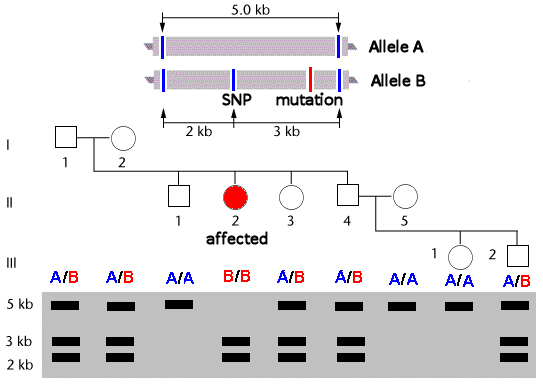
Use of an RFLP as
a co-dominant genetic marker
for a recessive trait
At a particular gene
locus, alleles A & B share two flanking SNP sites separated by 5
kbp (blue lines), and allele B has a third SNP 2 Kbp from the
5' end of the region.
This SNP is genetically
linked to a SNP mutation (red line) that produces a phenotypically
recessive trait. Because the distance between them is so
small, it is unlikely that the linkage will be broken by genetic
recombination.
A DNA sample
is taken from the test individual, and amplified by PCR so
as to include the whole region. If allele A is present,
there will be a single 5 kbp fragment. If allele
B is present, there will two fragments: the
middle SNP divides the 5 kbp fragment into two
fragments of 2 kbp and 3 kbp.
The middle SNP shows the presence
of the linked mutation, but does not cause
the trait. It is therefore described as a "marker" for the trait.
In the pedigree,
birth of individual II-2 with the recessive phenotype
indicates that the parents must both be heterozygotes: the other
unaffected sibs seek genetic counseling to determine if they may
be carriers. The genetic tests shows that two (II-3 &
II-4) are carriers, and that one of the two children of
the latter (III-2) is
also a carrier.

