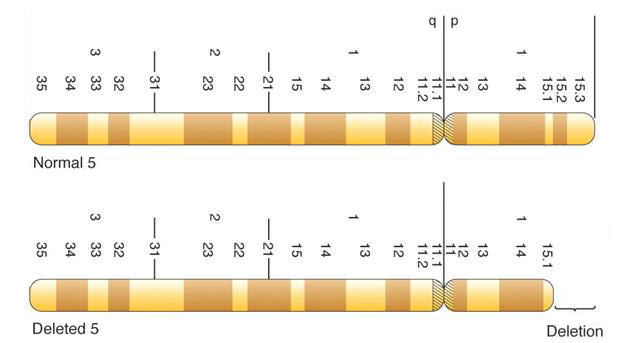
Segmental Aneuploidy: Cri-du-Chat Syndrome
Cri-du-Chat syndrome is the result of a
segmental
aneuploid deletion of the distal portion of the short
arm (2n=46,5p-)
of Chromosome 5.
The phenotype includes a characteristic high-pitched cry
("cat cry"),
low birth weight, poor muscle tone, microcephaly, and
retarded mental development. Children respond well to a
home environment, plus occupational, speech, and
physical therapies. Institutionalization is now less
common than formerly.
See [http://www.fivepminus.org/photos.htm#]

Abby, Nichole, & Tanner