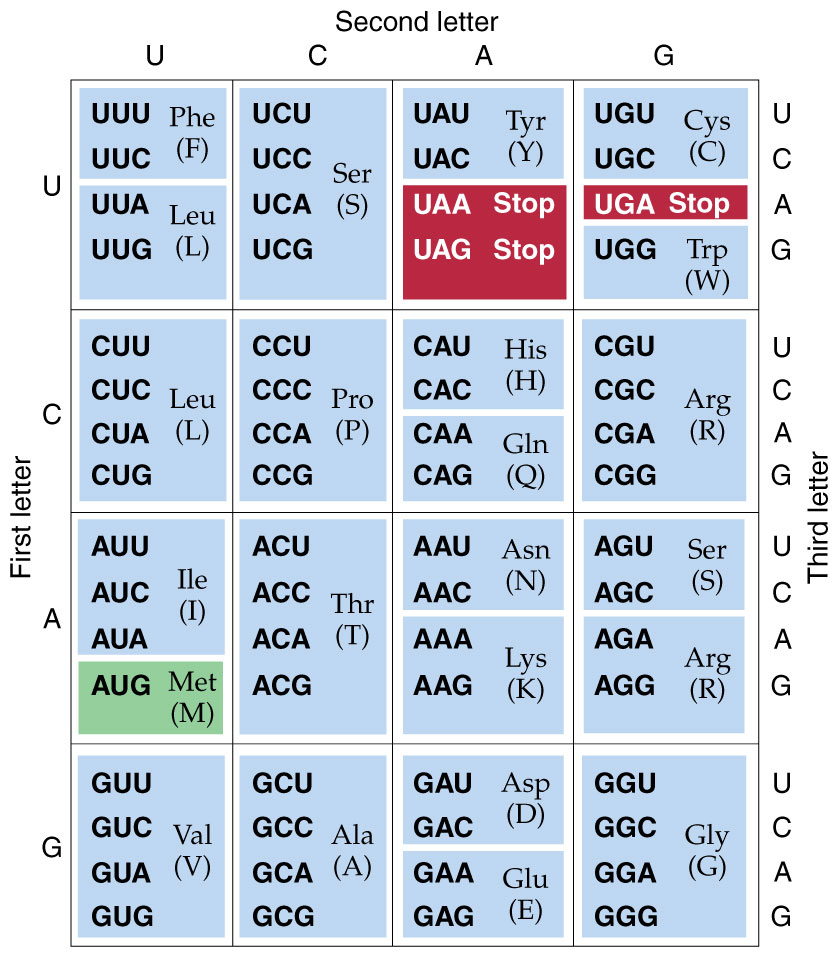
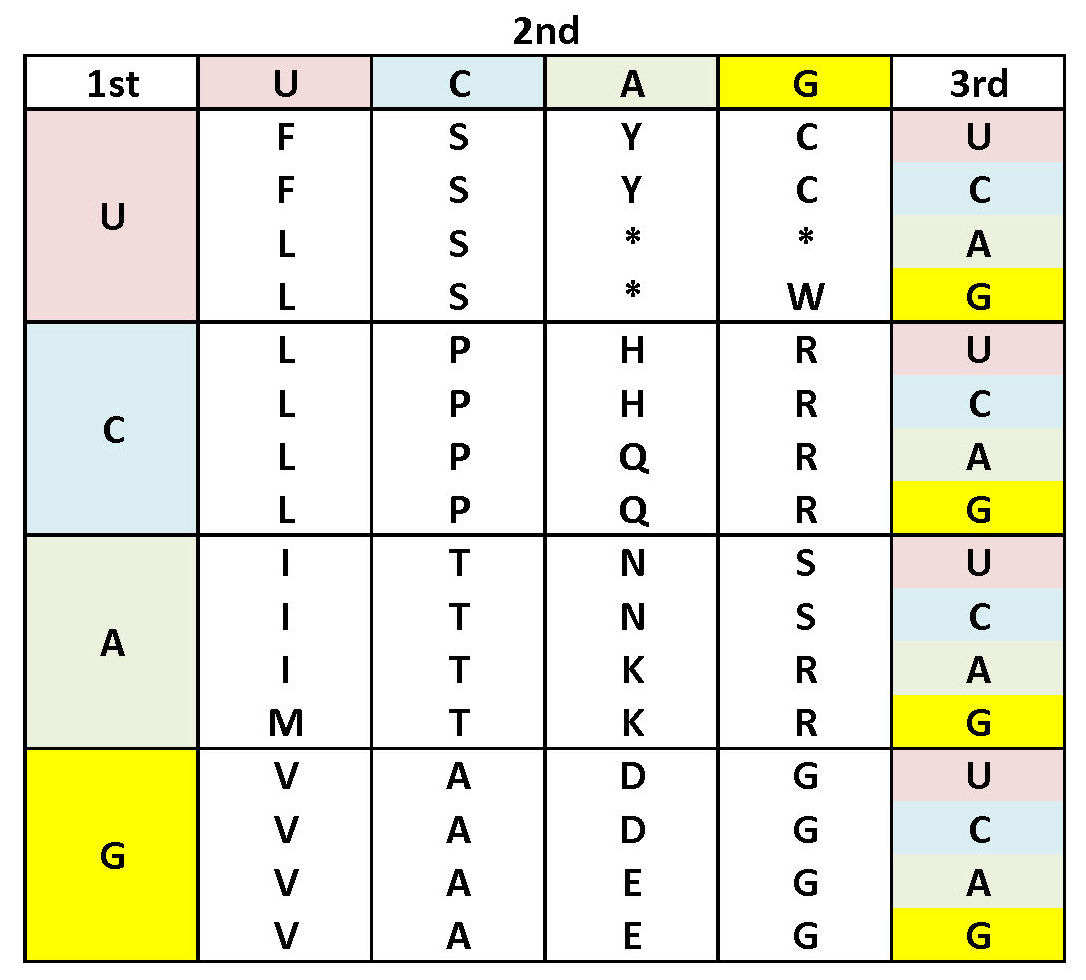
The "Universal" Genetic Code
The genetic code is a messenger RNA (mRNA)
code. Each of the 64 triplet codons in the table is
read 5'  3'.
The table is organized such that the first letter in the
codon is read in the four blocks at the left, the second
letter in the four columns across the top, and the third
letter as a line in each block of four. The code tables
above and below uses the IUPAC three- and single-letter
abbreviations for amino acids; Stop codons are
indicated as Stars (*).
3'.
The table is organized such that the first letter in the
codon is read in the four blocks at the left, the second
letter in the four columns across the top, and the third
letter as a line in each block of four. The code tables
above and below uses the IUPAC three- and single-letter
abbreviations for amino acids; Stop codons are
indicated as Stars (*).
Though this code is called "Universal", in fact NCBI now lists 27 different codes, for different evolutionary lineages or for organelles within those lineages. The most important of these for this course is the vertebrate mtDNA code, because many of the DNA sequences used in examples are from vertebrate mtDNAs.
Though this code is called "Universal", in fact NCBI now lists 27 different codes, for different evolutionary lineages or for organelles within those lineages. The most important of these for this course is the vertebrate mtDNA code, because many of the DNA sequences used in examples are from vertebrate mtDNAs.
Top figure © 2012 TA Brown, Introduction
to Genetics (3rd ed.); Bottom figure
and text © 2024 by Steven M.
Carr