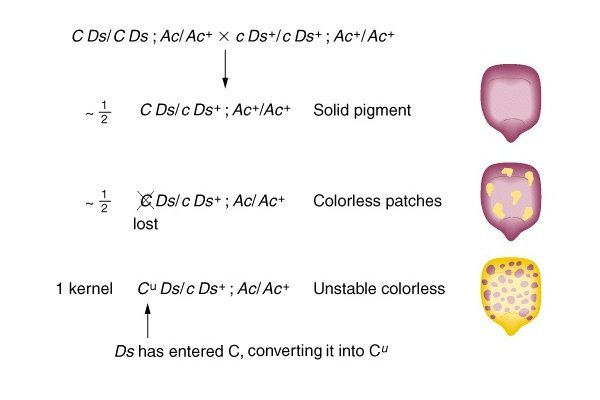
Genetic consequences of unstable Ds transposition in maize (Zea)

In the indicated
cross, C and c are alternate alleles at a
locus that determines seed coat color. C produces anthocyanin-pigmented (purple)
seeds, c produces colorless
(yellow) seeds. The parents are both double homozygotes: one is
C Ds // C Ds
and the other c Ds+
// c Ds+ thus all of the
offspring are C Ds // c Ds+
trans double heterozygotes. The dominant C allele is closely linked to the Ds (Dissociator)
element, and the recessive c
allele linked to the wild-type Ds+
(that is, no element). The Ac locus is
on another chromosome pair. The first parent is also an Ac+Ac heterozygote
with an Ac (Activator) element on one
chromosome. The second
parent is an Ac+Ac+
homozygous,
with no Ac
element. The Mendelian
expectation is that half of the offspring seeds will be Ac+Ac+
and half
Ac+Ac.
[Instructor: remember that Ds+ and Ac+
are the wildtype absence of Dissociator and Activator
elements, respectively. Student: You said that before.
Instructor: Yes, but you had forgotten it. Student: Nope.
Instructor: Very well, let's continue]
In the absence
of an Ac element
[top], the Ds element is stable: the C allele dominates c, and a uniform pigmented seed results.
In the presence of the Ac element [middle], the Ds element can "jump" and produce a chromosome break and loss of the linked C. In each cell where this occurs, the c allele on the alternate chromosome is now expressed as a colorless patch against a pigmented background. The timing of the break determines the size of the patch: early breaks produce larger patches.
In one unusual
kernel with the same genotype
[bottom], Ds has "jumped" into the
middle of the C locus very
early in the formation of the kernel, converting it to a Cu ("c unstable") allele
without breaking the chromosome. The Cuc combination is expressed as a
uniformly colorless seed. If Ds subsequently "jumps
out" again, the Cu
allele reverts to C, and the Cc
combination is expressed as a colored patch against the
colorless background. Early
breaks produce larger patches. Though the genotypes are
identical, the phenotypes are the reverse of each other. [See
also explanation of panels E &
F from Federoff (2012)]