Practice
trihybrid
crosses
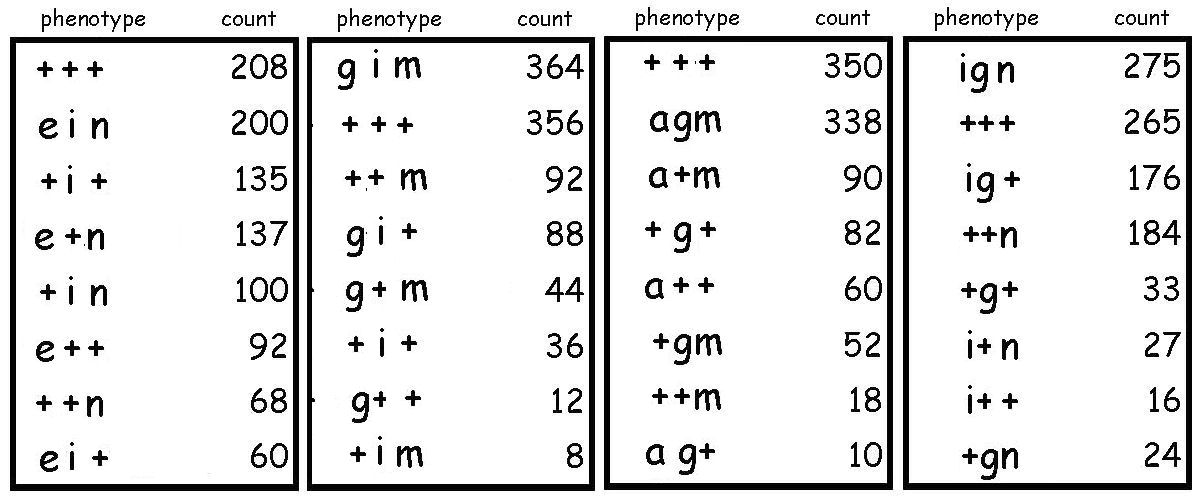
A)
The four sets of data above form a continuous map over six loci.
1) Determine the locus order and distances
among
loci for each set of data.
2) Determine the gene order and the distances
between all six loci.
In each case, a triple dominant homozygote parent
(ABD // ABD) has
been crossed
with a triple recessive homozygote tester
(abd // abd) to
produce
an F1 triple
heterozygote (AaBbDd). The
heterozygote was then
back-crossed to the tester strain
(abd // abd), and the numbers of resultant progeny
counted. A '+'
symbol indicates the phenotype corresponding to the dominant
allele at each locus. So, each parental cross can also be written
in
the form a+b+d+
// a+b+d+
X abd
// abd , or in short-hand form +++ // +++ X abd // abd .
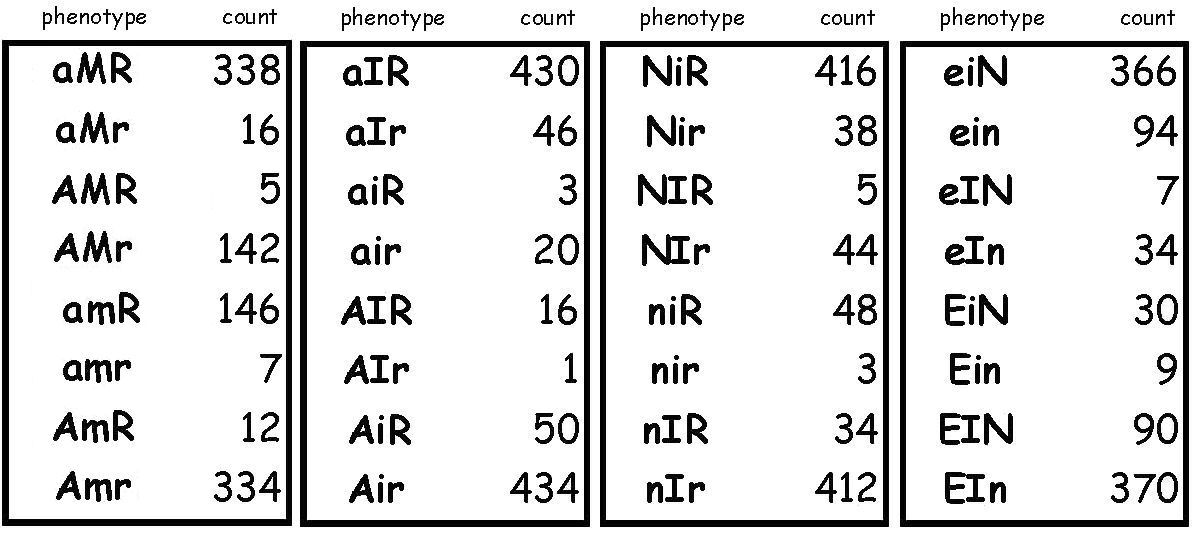
B) The four sets of data above form a
continuous map over six loci.
1) Determine the locus order and distances
among
loci for each set of data.
2) Determine the gene order and the distances
between all six loci.
Each of the P parents is
a triple homozygote as
above, however
the cis / trans
phase
relationships among the three loci in the various crosses are not
as
simple as in the first set of examples. The F1 offspring were
crossed with a
triple recessive homozygote, as above.
Hints:
First determine the Parental and Double Recombinant
phenotypes. All
distances in both maps should work out to round numbers. The
correct
gene order should spell a word.
All text
material
©2012 by Steven M. Carr


