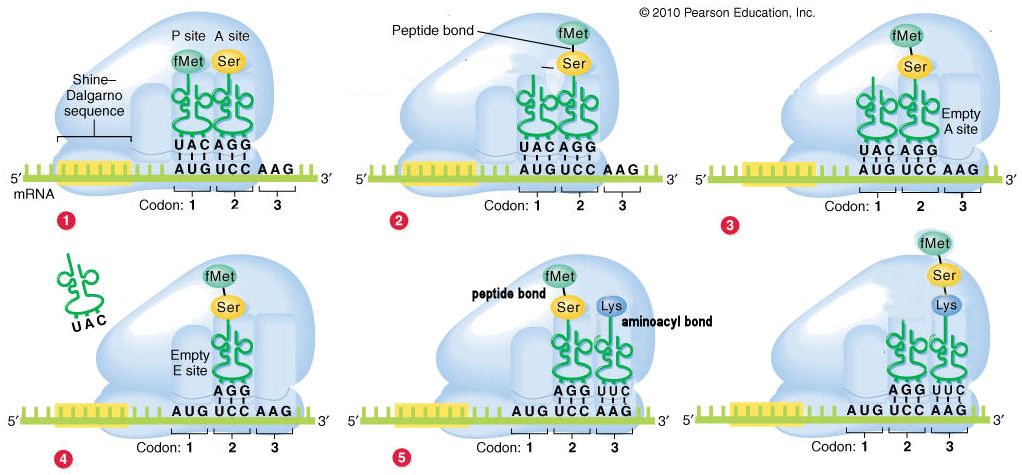
Stepwise elongation of polypeptide chains
The
diagram presents the messenger RNA (mRNA)
molecule as "fixed", with the 5' 3'
direction oriented left to right". The Ribosome "moves"
along the message from left to right, thus the mRNA is
read 5'
3'
direction oriented left to right". The Ribosome "moves"
along the message from left to right, thus the mRNA is
read 5' 3'
[or, the mRNA passes through the Ribosome in
the 5'
3'
[or, the mRNA passes through the Ribosome in
the 5' 3'
direction]. Note that the
Ribosome has already encountered the Shine-Delgarno
promoter sequence in the mRNA.
3'
direction]. Note that the
Ribosome has already encountered the Shine-Delgarno
promoter sequence in the mRNA.
Given this
orientation, the diagram therefore shows the left-to-right
order of the Exit, Peptidyl, & Aminoacyl sites
as EPA. However,
the functional order is APE, since
successive tRNAs enter through the A site,
pass to the P site, and exit from the E site.
(1) The fMet-tRNA
that initiates the process is shown already in
the P site. The next charged tRNA enter
the A site.
(2) The fMet is cleaved from
the tRNA in the
P site, and
linked by a peptide bond
to the amino acid in the A
site.
(3) The tRNA
in the P sites
moves to the E site, and the tRNA in the A site with the
di-peptide moves to the P site.
(4) The uncharged tRNA is released from the
E site.
(5)
A new charged tRNA enters
the A site. At this
point, the P site contains a peptidyl
bond, and the A site an aminoacyl
bond.
(6) The di-peptide is cleaved from the tRNA in the P site, and linked by a
peptide bond to the amino acid in the A site (as in step 2
above). This produces a tri-peptide in the A site.
The cycle continues in this manner. The tRNAs
in the P and A sites shift to the E
and P sites, the uncharged tRNA in the E
site drops out, a new tRNA with the amino acid
for the next codon enters the A sites, and so on.
Transfer
of the amino acid from the first tRNA to the second tRNA may
at first seem counter-intuitive. This however ensures that
the original amino terminus of the first amino
acid always remains
unmodified: thus the polypeptide "grows" in the amino  carboxy
(N
carboxy
(N C).
C).