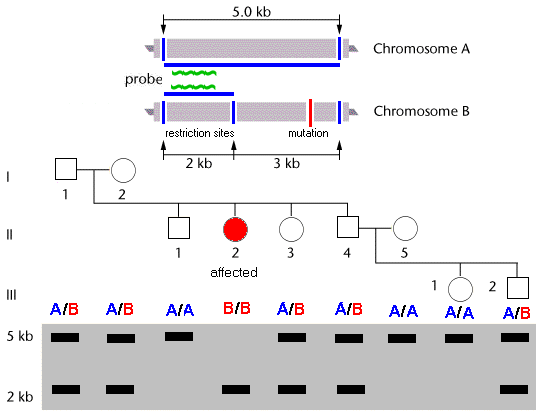
Use of an RFLP as a
co-dominant genetic marker
for a recessive trait
At a particular gene
locus, alleles A & B share two flanking restriction
sites (blue lines), and allele B has an extra restriction site in the middle of
the gene. The middle
restriction site in allele B is genetically linked to a DNA mutation (red line) that produces a phenotypically recessive
trait. [The middle site
is linked in cis to the mutation]
In the RFLP test,
DNA is extracted from the
test individual, and run out in a Southern Blot. A radioactive
probe is hybridized to the blot. The probe will anneal to
the 5' end of the region:
this will identify a 5Kb fragment
in the autoradiogram, if allele A is present. If
allele B is present, the middle restriction site cuts off
3Kb from the right-hand, 3' end of the fragment, so that the probe lights
up only the 5' 2Kb
fragment. The 3Kb fragment, which includes the
mutation, will not be
seen. Thus the 2kb fragment in the autoradiogram shows
the presence of the linked mutation, but does not
cause the trait. It is therefore a "marker"
for the trait.
An alternative technical approach is to use the
Polymerase Chain Reaction to amplify a region that includes
the 5kb region between the two outside restriction sites.
The product is cut with the same restriction enzyme as before, and
run out in an electrophoretic gel. In the absence of the mutation,
a
5kb band is expected. If the mutation is present, a pair
of 2kb and 3kb bands will be seen. This
procedure is much faster, and avoids the use of radioactive DNA
probes.
In the pedigree,
birth of individual II-2 with the recessive phenotype
indicates that the parents must both be heterozygotes. The
other, unaffected sibs seek genetic counseling to
determine if they may be carriers. The genetic tests shows that
two (II-3 & II-4) are heterozygous carriers,
and that one of the two children of the latter (III-2) is also a carrier.
Homework:
Suppose the PCR test
outlined above is used, and that the mutation occurs 2.5 kb from the
middle restriction
site and 0.5 kb from the right-hand restriction site.
How many bands would you
expect to see in the heterozygote?
Draw the expected gel
result. Explain.

