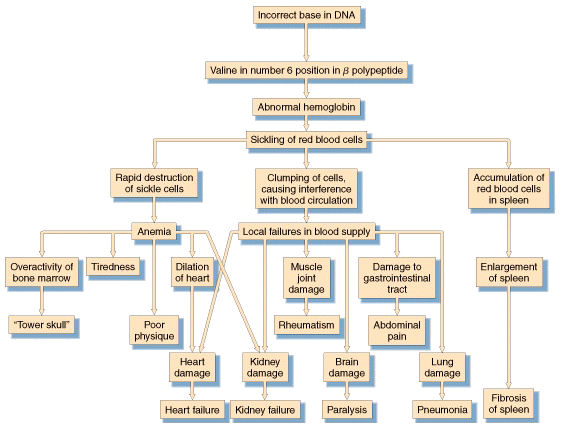
Pleiotropic
consequences of
nucleotide
substitution in the Beta-Hemoglobin gene
Pleiotropy is the phenomenon of secondary,
tertiary, and more remote consequences of gene expression
or a gene
mutation. In the
case of of the sickle-cell mutation, a single-base
mutation alters the
sequence of amino acids in the beta-hemoglobin that
directly results in sickle-cell anemia, which produces
pleiotropic effects in the circulatory
system, spleen, and overall physical appearance.
Figure © 2000 by Griffiths et al. ; text © 2012 by Steven M. Carr