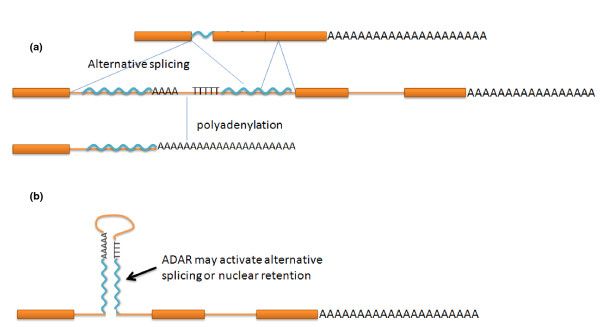
Alu elements and post-transcriptional processing of transcripts.
The majority of human genes include transposable Alu
repetitive elements in their introns.
These elements are bounded by AAAA and TTTT
sequences, which allow both transposition among
introns and formation of hairpin loops. If these
sequences accumulate mutations, they may wrongly signal
transcriptional processing events, which can result in alternative
splicing of exons and (or) altered polyadenylation,
which may affect gene function.